What is cloaking?
In SEO, cloaking is the practice of showing a different page to search engine crawlers than to users. This makes it possible to show pages with different content, different links, or even completely different pages, allowing website owners to manipulate a website’s rankings in the SERPs.
When different content is served to search engine crawlers than to normal website visitors, cloaking is generally considered a black hat SEO practice by search engines.
Search engine guidelines and cloaking
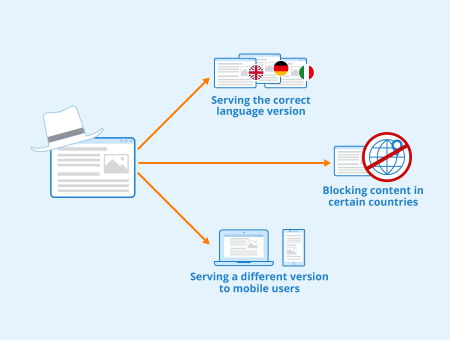
When different content is served to search engines and normal users, cloaking is always considered against search engine guidelines. However, Google has stated that cloaking is only against guidelines when specifically targeting their crawler and may not be considered black hat if it has been done to improve the user experience of a website.[1]
There are instances where serving different content to different users can be beneficial for the user experience and therefore isn’t against their guidelines. For example:
- Automatically serving the correct language version based on the IP-address of a user.
- Serving a different version to mobile users than to desktop users
- Blocking content in certain countries in order to comply with data protection regulations
Cloaking in black hat SEO
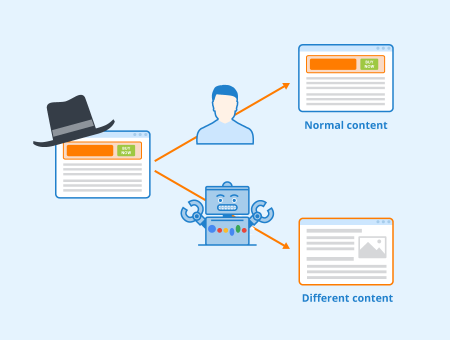
In black hat SEO, cloaking can be used to manipulate the search engines and rank pages for keywords that it otherwise would not rank for. However, it has lost a lot of its effectiveness since first implemented in the early days of search in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Currently, cloaking is penalized by Google and other major search engines when discovered. This means that although cloaking may provide a temporary result, the chances of a site getting penalized grow substantially.
Cloaking that targets search engine crawlers has no place in white hat SEO, although cloaking for user experience improvements, like serving different language versions or different mobile/PC versions of a website, is considered white hat.
Different forms of cloaking
IP-cloaking
IP-cloaking serves different pages or different content based on IP-addresses. For example, serving a different page to users on IP-addresses related to Google.
User-Agent cloaking
User-Agent cloaking serves a different webpage or different content to search engines based on the User-Agent.
HTTP REFERER cloaking
HTTP Referer cloaking shows a different page or different content based on the HTTP referer sent by the web browser.
Javascript cloaking
Javascript cloaking takes advantage of how Googlebot, as well as different browsers, process Javascript, hiding or manipulating certain content on a page based on this..
Relevance to SEO
Cloaking used to be extremely effective in the early days of SEO but is currently penalized by search engines. In SEO, it’s important to avoid cloaking issues, but also prevent any accidental cloaking by the use of technologies/code that search engines have trouble reading.
References
Related links
- https://developers.google.com/search/docs/advanced/guidelines/cloaking
- https://www.searchenginewatch.com/2011/11/04/cloaking-a-guide-from-google/
Similar articles
